What is a Fullstack Developer?
Broadly speaking, a person in software engineering who has a good working knowledge of developing and delivering software across the full software / hardware solution stack who specialises in a number of areas.
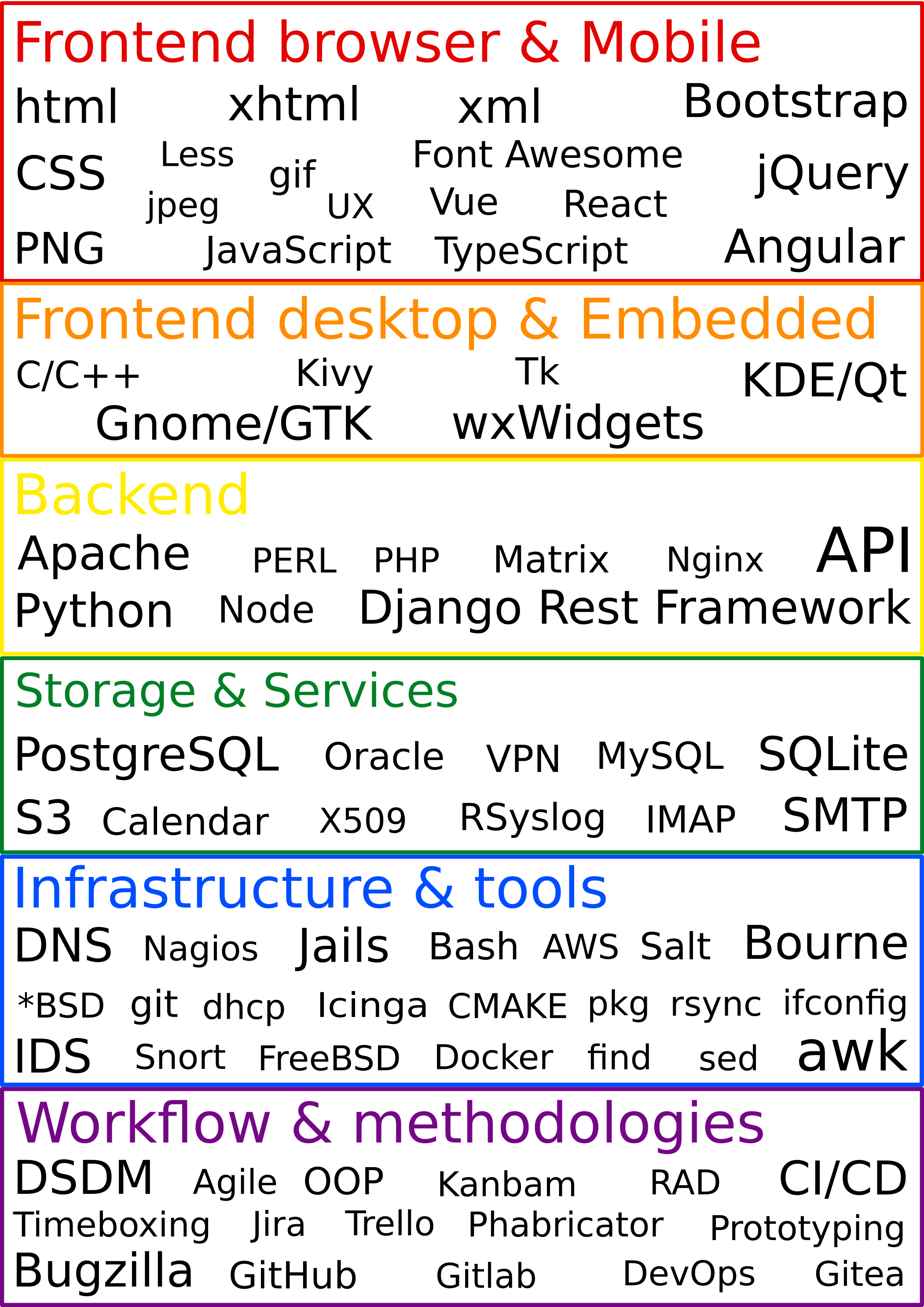
Full-stack Developers can offer significant benefits when researching, planning and starting projects due to their extensive and in-depth knowledge and experience.
Tech stack / solution stack?
It's a long time since the acronym LAMP, for working with Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP had any useful meaning as the components have always included the BSDs, PERL, PostgreSQL and many others.
Increasingly languages, subsystems and components, known as Solution stacks, are whole, interoperable and highly specialised ecosystems. Applications are often described as "running on top of" a stack. Although many components are interoperable, there are often tech stacks that work well together and can serve as a useful starting point.
As the cost of changing components after a project has started increase as it progresses, it's usually cost effective to plan longer term and build in objectives early on to ensure smoother transitions.
Frontend / Backend?
Although these terms are often used to describe the user facing presentation side of an application and the functional aspect that provides services to the front end and ultimately delivers the business application, increasingly these are just two visible aspects of a more complex ecosystem as the above image shows.
What is software development?
There are many approaches to software development, Deborah Kurata described her GUIDS methodology:
- Goal-centered design;
- User-interface design;
- Implementation-centered design;
- Data-design;
- Strategies for construction.
These steps are processes within the architecture phase. Modelling, though not a step in the architecture, can be incorporated into the first for design steps.
Erling S. Andersen, Kristoffer V Grude and Tor Haug in their Goal Directed Project Management have a useful People, System and Organization perspective allowing the people and organisation involved in developing simultaneously with the system.
More recently five main stages of software development can be identified as:
- Requirements
- Design
- Construction
- Testing
- Maintenance
Methodologies such as Agile/DSDM/Kanban tend to combine the first four into highly capable and focussed projects delivering much faster than traditional waterfall projects.